 It is a Japanese term that suggests continuous improvement where “Kai” means continuous and “Zen” means improvement. Others translation predicts “Kai” means change and “Zen” means for the better. Basically, it is a Japanese philosophy that aims at continuous improvement throughout all aspects of life.
It is a Japanese term that suggests continuous improvement where “Kai” means continuous and “Zen” means improvement. Others translation predicts “Kai” means change and “Zen” means for the better. Basically, it is a Japanese philosophy that aims at continuous improvement throughout all aspects of life.
Kaizen activities lead to continuous improvement across all business functions including manufacturing to management. It eliminates waste by improving standardized activities and processes. As per the modern usage, a “kaizen blitz” or “kaizen event” is a set of activities that is designed to address a particular issue over the course of a week. It is limited in scope.
Kaizen is a process that humanizes the workplace, eliminates overly hard work and focuses on applying the scientific method while performing experiments and aims at identifying and eliminating waste in business processes. The philosophy suggests that daily activities of business procedures should effectively implement kaizen principles.
The cycle of kaizen activity comprises of following activities:
(1) Standardizing an operation
(2) Measuring the standardized operation (find cycle time and amount of in-process inventory)
(3) Gauging measurements against requirements
(4) Displaying creativity to meet requirements and increase productivity
(5) Standardizing the new, improved operations
(6) Continuing the cycle ad infinitum.
Integration of Six Sigma, Lean and Kaizen in a business project leads to breakthrough improvement. Leadership, creativity, and innovation are the chief drivers of growth in any organization. Every strategic improvement initiative requires the following elements
Leadership, Creativity, and Innovation: This element drives the cultural change, mentors the organization and leads to the alignment of the strategy and deployment. By integrating the Six Sigma, Lean, and Kaizen, leadership team can provide clearer focus on improving profitability and competitiveness.
Teaming and Employee Involvement: This element suggests that people need to be equipped with the right tools and they should be empowered to take responsible actions to drive the growth.
Closed-Loop Performance: This element includes real time performance measurement that allows the people to understand the cause-and-effect relationship between their actions and the improvement goals.
 Total Quality Management is a concept that focuses on continuous improvement of work in all areas by high level strategic planning, decision making and executing the details. It results in improvement in people, processes and technology. It is evolved in the 1950’s and popularized in 1980’s.
Total Quality Management is a concept that focuses on continuous improvement of work in all areas by high level strategic planning, decision making and executing the details. It results in improvement in people, processes and technology. It is evolved in the 1950’s and popularized in 1980’s. In order to grow and exceed bottom lines expectations consistently, companies are required to learn the basics of Lean Six Sigma thoroughly. In a global competitive manufacturing environment, companies are spending thousands of dollars in pursuing the Materials Required Planning and Enterprise Resource Planning, however they still face decline in growth and profits.
In order to grow and exceed bottom lines expectations consistently, companies are required to learn the basics of Lean Six Sigma thoroughly. In a global competitive manufacturing environment, companies are spending thousands of dollars in pursuing the Materials Required Planning and Enterprise Resource Planning, however they still face decline in growth and profits. The successful implementation of the Six Sigma methodology requires that the senior leaderships plays a vital role in the aligning the entire organization and inculcate the Six Sigma culture. Committed leadership involving senior executives, master black belts, black belts, and green belts works closely and challenges effectively.
The successful implementation of the Six Sigma methodology requires that the senior leaderships plays a vital role in the aligning the entire organization and inculcate the Six Sigma culture. Committed leadership involving senior executives, master black belts, black belts, and green belts works closely and challenges effectively. Lean dynamics is a practice of business management that focuses on eliminating wasteful expenditure of resources by emphasizing on the dynamic business conditions that leads to the accumulation of wastes in the first place.
Lean dynamics is a practice of business management that focuses on eliminating wasteful expenditure of resources by emphasizing on the dynamic business conditions that leads to the accumulation of wastes in the first place. Lean manufacturing is a practice that identifies the non value added activities that is considered as waste from the perspective of the customers and focuses on eliminating them. Here customer is anyone who consumes a product or uses as service and value defines the process for which customer would be willing to pay.
Lean manufacturing is a practice that identifies the non value added activities that is considered as waste from the perspective of the customers and focuses on eliminating them. Here customer is anyone who consumes a product or uses as service and value defines the process for which customer would be willing to pay. In simple terms, Lean Six Sigma is a methodology which combines the business improvement methods of Lean manufacturing practice and Six Sigma process. Lean practice focuses on speed of the process while Six Sigma relies on quality. Therefore by the fusion of both the practices we have Lean Six Sigma which provides speed and quality to the customers. It leads to faster improvement in the business processes relating to customer satisfaction, quality and cost.
In simple terms, Lean Six Sigma is a methodology which combines the business improvement methods of Lean manufacturing practice and Six Sigma process. Lean practice focuses on speed of the process while Six Sigma relies on quality. Therefore by the fusion of both the practices we have Lean Six Sigma which provides speed and quality to the customers. It leads to faster improvement in the business processes relating to customer satisfaction, quality and cost. In an organization, at the time of production of a product six sigma methodology is implemented in order to avoid defects and wastes and make sure that the product meets the customer satisfaction. At the time of six sigma quality improvement, a lot of money is at the risk point and if unproductive changes are taken or made, it leads to lot of loss to the company in both the finance and productive aspects. In order to avoid such a loss, it is that important in a business to test the efficacy of the changes made. This test can be done with the help of hypothesis tools and testing.
In an organization, at the time of production of a product six sigma methodology is implemented in order to avoid defects and wastes and make sure that the product meets the customer satisfaction. At the time of six sigma quality improvement, a lot of money is at the risk point and if unproductive changes are taken or made, it leads to lot of loss to the company in both the finance and productive aspects. In order to avoid such a loss, it is that important in a business to test the efficacy of the changes made. This test can be done with the help of hypothesis tools and testing. The main aim of the implementation of six sigma in to a project team is to define the correct testing parameter. The faults in defining the objectives and the testing parameters, results in difficulty to ensure the success of the proposed changes. Even a small fault in the proposed change can result severely in the business process where it is being implemented. So it is better to use the hypothesis testing for attaining the accurate results of the testing.
The main aim of the implementation of six sigma in to a project team is to define the correct testing parameter. The faults in defining the objectives and the testing parameters, results in difficulty to ensure the success of the proposed changes. Even a small fault in the proposed change can result severely in the business process where it is being implemented. So it is better to use the hypothesis testing for attaining the accurate results of the testing. Apart form the above advantages there are limitation for the using of hypothesis testing, in testing the effectiveness of a proposed changes. This is because, there are even many more factors that can affect a business process. Some of these factors are employee dissatisfaction, changes in the technology etc which cannot be tested with the help of hypothesis testing. There fore it is the duty of the analyst to make sufficient arrangements for all these types of testing and these test results can be used to compare with the hypothesis results to find out a proposed change, which confirms to suggested hypothesis.
Apart form the above advantages there are limitation for the using of hypothesis testing, in testing the effectiveness of a proposed changes. This is because, there are even many more factors that can affect a business process. Some of these factors are employee dissatisfaction, changes in the technology etc which cannot be tested with the help of hypothesis testing. There fore it is the duty of the analyst to make sufficient arrangements for all these types of testing and these test results can be used to compare with the hypothesis results to find out a proposed change, which confirms to suggested hypothesis. With in an organization, the objective is the long-term improvement of its processes in order to enhance the performance of the organization and the products, gain the interest of the customers, employees and shareholders, and thus sustain in the world of global marker competitive. Still just improving a process is not a complete business option, but a complete process re-design is required.
With in an organization, the objective is the long-term improvement of its processes in order to enhance the performance of the organization and the products, gain the interest of the customers, employees and shareholders, and thus sustain in the world of global marker competitive. Still just improving a process is not a complete business option, but a complete process re-design is required. It is better to replace DMADV, than the other way. There are two occasions in which DMADV can be used to replace DMAIC. One occasion is at the time there is no existing product, out of which the organization is aiming to create from the scratch. At the time when the implementation of DMAIC has not produced the expected result, though best efforts are done to make the improvements, DMADV methods can be used. It is proved that there are situations where planned DMAIC is been replaced by the use of DMADV method. The method is used at the time when the “improvement” process is not able to deliver the organization the expectations.
It is better to replace DMADV, than the other way. There are two occasions in which DMADV can be used to replace DMAIC. One occasion is at the time there is no existing product, out of which the organization is aiming to create from the scratch. At the time when the implementation of DMAIC has not produced the expected result, though best efforts are done to make the improvements, DMADV methods can be used. It is proved that there are situations where planned DMAIC is been replaced by the use of DMADV method. The method is used at the time when the “improvement” process is not able to deliver the organization the expectations.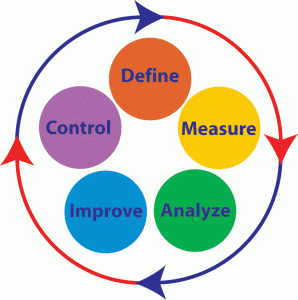 Six Sigma is an data driven approach used by many organizations that strives to achieve quality & perfection. It is a methodology used to eliminate defects & to determine the performance of the process. A defect is anything that is outside or against customer requirements. To achieve this, a process should not produce defects more than 3.4 per million opportunities.
Six Sigma is an data driven approach used by many organizations that strives to achieve quality & perfection. It is a methodology used to eliminate defects & to determine the performance of the process. A defect is anything that is outside or against customer requirements. To achieve this, a process should not produce defects more than 3.4 per million opportunities.